State University System of Florida
| State University System of Florida |
|
|---|---|
Seal of the State of Florida |
|
| Established | 1954 |
| Type | Public university system |
| Endowment | $2.92 billion (Combined) |
| Chancellor | Frank T. Brogan |
| Students | 302,513(Fall 2008)[1] |
| Location | Tallahassee, FL, USA |
| Campus | 11 Member Institutions |
| Website | Official website |
The State University System of Florida (SUS, or SUSF out-of-state) is a system of eleven public universities in the U.S. state of Florida. As of 2011, over 320,000 students were enrolled in Florida's state universities. Together with the Florida College System, which includes Florida's 28 community colleges and state colleges, it is part of Florida's system of public higher education. The system, headquartered in Tallahassee,[2] is overseen by a Chancellor and governed by the Florida Board of Governors.
The Florida Board of Governors was created in 2003 to centralize the administration of the State University System of Florida. Previously, Florida's State University System had been governed by the Florida Board of Regents (1965–2001) and the Florida Board of Control (1905–1965).
Contents |
History
Prior to 1905, Florida's state institutions were governed by a Board of Education and even earlier variations thereof, reaching back to the Florida Constitution of 1838 wherein higher education and normal education was established, based on grants of land from the U.S. Congress. From 1905 to 1965, the few universities in the system were governed by the Florida Board of Control. The Board of Control was replaced by the Florida Board of Regents in 1965, to accommodate the growing university system. The Board of Regents governed until it was disbanded by the Florida Legislature in 2001, and its authority was divided between the Florida Board of Education (which was given some authority over all levels of public education in the state), and appointed university boards of trustees, which operated independently for each separate institution. In 2002, Floridians led by U.S. Senator Bob Graham passed an amendment to the Florida Constitution establishing a new statewide governing body, the Florida Board of Governors.
During the 2008-2009 academic year, the State University System enrolled 301,135 total students. In total 233,772 undergraduates, and 56,872 graduate and professional students.[1]
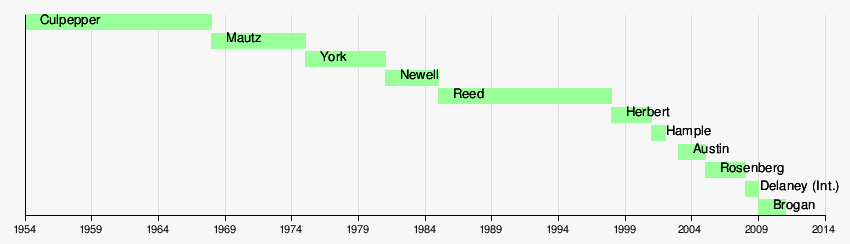
Chancellors of the State University System
| Term | Chancellor |
|---|---|
| 1954—1968 | J. Broward Culpepper |
| 1968—1975 | Robert B. Mautz |
| 1975—1980 | E.T. York |
| 1981—1985 | Barbara W. Newell |
| 1985—1998 | Charles B. Reed |
| 1998—2001 | Adam W. Herbert |
| 2001—2001 | Judy G. Hample |
| 2003—2005 | Debra D. Austin |
| 2005—2009 | Mark B. Rosenberg |
| 2009—2009 | John A. Delaney (interim) |
| 2009—Present | Frank T. Brogan |
 |
Member institutions
Colleges and universities
| Institution | Location | Established | Endowment | Acceptance Rate[3] | Enrollment[1] | Campus Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Florida A&M University | Tallahassee | 1887 | $119 million | 63% | 11,848 | 420 acres (1.7 km2) |
| Florida Atlantic University | Boca Raton | 1961 | $182 million[4] | 56% | 27,021 | 850 acres (3.4 km2) |
| Florida Gulf Coast University | Fort Myers | 1991 | $39 million | 76% | 12,024 | 760 acres (3.1 km2) |
| Florida International University | Miami | 1965 | $138 million[5] | 33%[6] | 44,010 | 573 acres (2.3 km2) |
| Florida State University | Tallahassee | 1851[7] | $571 million[8] | 42%[9] | 40,838 | 1,392 acres (5.6 km2)[10] |
| New College of Florida | Sarasota | 1960 | $33 million[11] | 57% | 787 | 144 acres (0.6 km2) |
| University of Central Florida | Orlando | 1963[12] | $114 million[12] | 43%[12] | 56,235 | 1,415 acres (5.7 km2)[12] |
| University of Florida | Gainesville | 1853[13] | $1.1 billion[14] | 37% | 50,116 | 2,000 acres (8.1 km2) |
| University of North Florida | Jacksonville | 1969 | $95 million[15] | 66% | 15,427 | 1,300 acres (5.3 km2) |
| University of South Florida | Tampa | 1956 | $360 million[16] | 49% | 47,122 | 1,913 acres (7.7 km2) |
| University of West Florida | Pensacola | 1963 | $61 million[17] | 70% | 12,176 | 1,600 acres (6.5 km2) |
Independent research units
| Institution | Location | Established |
|---|---|---|
| Florida Institute of Oceanography | St. Petersburg | 1967 |
| University Press of Florida | Gainesville | 1945 |
Research and enrollment
| Institutions | Research expenditure (2007)[18] | Enrollment (Fall 2008)[1] |
|---|---|---|
| Florida A&M University | $17.6 million | 11,848 |
| Florida Atlantic University | $27.3 million | 27,021 |
| Florida Gulf Coast University | $11.8 million | 10,238 |
| Florida International University | $89.1 million | 39,146 |
| Florida State University | $211.3 million | 39,072 |
| University of Central Florida | $141.1 million | 50,275 |
| University of Florida | $635.9 million | 51,851 |
| University of North Florida | $8.4 million | 15,427 |
| University of South Florida | $337.1 million | 46,332 |
| University of West Florida | $14.9 million | 10,516 |
| Total | $1.49 billion | 302,513 |
Gallery
Student profile
| Students[1] | Florida[19] | U.S. Census[19] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 43% | 49.1% | 49.2% |
| Female | 57% | 50.9% | 50.8% |
| Not Reported | <1% | N/A | N/A |
| Students[1] | Florida[20] | U.S. Census[21] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| African American | 14% | 16% | 12.4% |
| Asian American | 5% | 2.1% | 4.3% |
| European American | 57% | 63.1% | 74.1% |
| Hispanic American | 18% | 18% | 14.7% |
| Native American | <1% | 1.4% | 0.8% |
| International student | 4% | N/A | N/A |
| Not Reported | 2% | N/A | N/A |
| Test Scores[1] | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|
| ACT | 24.5 | 36 |
| SAT | 1156 | 1600* |
| GRE | 1089.4 | 1600 |
| Average High School GPA | 3.7 | N/A |
- NOTE: Most Florida universities do not take the new SAT writing section into consideration for admission purposes.
Library system
The State University of System of Florida operates one of the largest academic library systems in the world. It manages more than 18 million items.[22] Each campus maintains its own library catalog and also shares an agreement for library reciprocal borrowing. The agreement was called the Florida Distance Learning Iniative and was signed on February 9, 1999.[23]
The physical collections are scattered across each of the SUS campuses. Their collections and stand-alone library buildings are listed in the main article. Due to organizational differences, having more libraries does not directly translate into a higher volume of specific collections of materials.
Tuition differential
During Florida's 2007 Legislative Session, Governor Charlie Crist signed into law SB-1710 which allowed the Florida Board of Governors to charge Tuition Differential of 40% above and beyond the regular in-state undergraduate tuition rates for the University of Florida and Florida State University. In addition the University of South Florida was allowed to raise its rates 30% above and beyond the regular in-state undergraduate tuition charges. This was allowed because these three institutions reached Research Flagship benchmarks that the other universities in the State University System could not achieve.[24]
In 2008, in lieu of receiving increased research funding in excess of $100 million, the Tuition Differential was allowed to now include the University of Central Florida and Florida International University. These two institutions were allowed to raise their in-state undergraduate tuition rate 30% above and beyond the regular tuition rates. This legislation ultimately created a multi-tier system for higher education in Florida's State University System of Florida.[25]
In 2009, Governor Charlie Crist and the Florida Legislature passed an even broader tuition differential for all of the institutions within the State University System of Florida. The new provision allows for a 15 percent annually tuition increase for in-state undergraduate tuition until they reach the national average.[26][27] Governor Crist signed off on the legislation on June 1, 2009.[28]
The expanded tuition differential is not covered by the Bright Futures Scholarship Program, and the stipulation states that 30 percent of the added revenue must go to need-based student financial aid.[29] This legislation was passed due to severe budget constraints caused by the Florida economy.[30]
Notable alumni and attendees
See also
- Florida
- Education in Florida
- Florida College System
- Florida Board of Regents
- Florida Board of Control
- Florida Board of Governors
- Florida Student Association
- Florida Department of Education
- Bright Futures Scholarship Program
- Advisory Council of Faculty Senates
- List of colleges and universities in Florida
References
- ^ a b c d e f g 2009 SUSF Quick Facts
- ^ "Contact Us." State University System of Florida. Retrieved on August 26, 2011. "Florida Board of Governors State University System 325 West Gaines Street, Suite 1614 Tallahassee, Fl 32399-0400"
- ^ US News retrieved on 04-13-2009.
- ^ FAU NACUBO info
- ^ FIU endowment info
- ^ http://w3.fiu.edu/irdata/portal/quickfacts.htm
- ^ "State Library and Archives of Florida - The Florida Memory Project Timeline (see 1851)". http://www.floridamemory.com/Timeline. Retrieved 2009-03-06.
- ^ FSU NACUBO info
- ^ FSU Acceptance rate
- ^ "Florida State University Summary of University Properties". http://www.fpc.fsu.edu/sitesum.html. Retrieved 2009-03-06.
- ^ New College NACUBO info
- ^ a b c d "Facts About UCF". UCF Office of Institutional Research. http://www.iroffice.ucf.edu/character/current.html. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ^ "University of Florida Website". http://www.ufl.edu/aboutUF/. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ UF NACUBO info
- ^ UNF NACUBO info
- ^ USF NACUBO info
- ^ UWF NACUBO info
- ^ SUSF Facts
- ^ a b "Florida - Fact Sheet - American FactFinder". 2005-2007 American Community Survey 3-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/ACSSAFFFacts?_event=&geo_id=04000US12&_geoContext=01000US. Retrieved 2009-09-23.
- ^ See Demographics of Florida for references.
- ^ "B02001. RACE - Universe: TOTAL POPULATION". 2006 American Community Survey. United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-context=dt&-ds_name=ACS_2006_EST_G00_&-CONTEXT=dt&-mt_name=ACS_2006_EST_G2000_B02001&-tree_id=306&-redoLog=false&-currentselections=ACS_2006_EST_G2000_B02001&-currentselections=ACS_2006_EST_G2000_B02003&-currentselections=ACS_2006_EST_G2000_C02003&-geo_id=01000US&-geo_id=02000US1&-geo_id=02000US2&-geo_id=02000US3&-geo_id=02000US4&-search_results=01000US&-format=&-_lang=en. Retrieved 2009-09-21.
- ^ SUSF Resources - Libraries
- ^ SUS borrowing agreement
- ^ SB-1710
- ^ Orlando Sentinel "House measure would establish two-tier higher-education system" http://blogs.orlandosentinel.com/news_politics/2008/03/house-measure-w.html
- ^ Orlando Sentinel info
- ^ Senator Pruitt's legislation
- ^ Herald Tribune info about Crist signing increased tuition legislation
- ^ Governor Crist's press release
- ^ Florida Chamber of Commerce info about expanded tuition rates.However, if your account was opened before February 1, 2007 your account is excempt from paying the tuition differential fee.
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||